Computer-generated imagery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Computer-generated imagery (CGI) is a specific-technology or application of computer graphics for creating or improving images in
 Prior to CGI being prevalent in film, virtual reality, personal computing and gaming, one of the early practical applications of CGI was for aviation and military training namely, the flight simulator. Visual systems developed in flight simulators were also an important precursor to three dimensional computer graphics and Computer Generated Imagery (CGI) systems today. Namely because the object of flight simulation was to reproduce on the ground the behavior of an aircraft in flight. Much of this reproduction had to do with believable visual synthesis that mimicked reality. The Link Digital Image Generator (DIG) by the Singer Company (Singer-Link), was considered one of the worlds first generation CGI systems. It was a real-time, 3D capable, day/dusk/night system that was used by NASA shuttles, for F-111s, Black Hawk and the B-52. Link's Digital Image Generator had architecture to provide a visual system that realistically corresponded with the view of the pilot. The basic archictecture of the DIG and subsequent improvements contained a scene manager followed by geometric processor, video processor and into the display with the end goal of a visual system that processed realistic texture, shading, translucency capabilties, and free of aliasing.
Combined with the need to pair virtual synthesis with military level training requirements, CGI technologies applied in flight simulation were often years ahead of what would have been available in commercial computing or even in high budget film. Early CGI systems could depict only objects consisting of planar polygons. Advances in algorithms and electronics in flight simulator visual systems and CGI in the 1970s and 1980s influenced many technologies still used in modern CGI adding the ability to superimpose texture over the surfaces as well as transition imagery from one level of detail to the next one in a smooth manner.
The evolution of CGI led to the emergence of virtual cinematography in the 1990s, where the vision of the
Prior to CGI being prevalent in film, virtual reality, personal computing and gaming, one of the early practical applications of CGI was for aviation and military training namely, the flight simulator. Visual systems developed in flight simulators were also an important precursor to three dimensional computer graphics and Computer Generated Imagery (CGI) systems today. Namely because the object of flight simulation was to reproduce on the ground the behavior of an aircraft in flight. Much of this reproduction had to do with believable visual synthesis that mimicked reality. The Link Digital Image Generator (DIG) by the Singer Company (Singer-Link), was considered one of the worlds first generation CGI systems. It was a real-time, 3D capable, day/dusk/night system that was used by NASA shuttles, for F-111s, Black Hawk and the B-52. Link's Digital Image Generator had architecture to provide a visual system that realistically corresponded with the view of the pilot. The basic archictecture of the DIG and subsequent improvements contained a scene manager followed by geometric processor, video processor and into the display with the end goal of a visual system that processed realistic texture, shading, translucency capabilties, and free of aliasing.
Combined with the need to pair virtual synthesis with military level training requirements, CGI technologies applied in flight simulation were often years ahead of what would have been available in commercial computing or even in high budget film. Early CGI systems could depict only objects consisting of planar polygons. Advances in algorithms and electronics in flight simulator visual systems and CGI in the 1970s and 1980s influenced many technologies still used in modern CGI adding the ability to superimpose texture over the surfaces as well as transition imagery from one level of detail to the next one in a smooth manner.
The evolution of CGI led to the emergence of virtual cinematography in the 1990s, where the vision of the
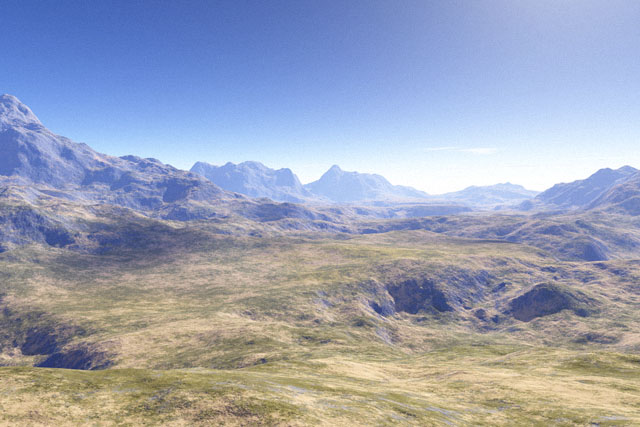 Not only do animated images form part of computer-generated imagery; natural looking landscapes (such as
Not only do animated images form part of computer-generated imagery; natural looking landscapes (such as
 Modern architects use services from computer graphic firms to create 3-dimensional models for both customers and builders. These computer generated models can be more accurate than traditional drawings.
Modern architects use services from computer graphic firms to create 3-dimensional models for both customers and builders. These computer generated models can be more accurate than traditional drawings.
 Computer generated models used in skeletal animation are not always anatomically correct. However, organizations such as the
Computer generated models used in skeletal animation are not always anatomically correct. However, organizations such as the
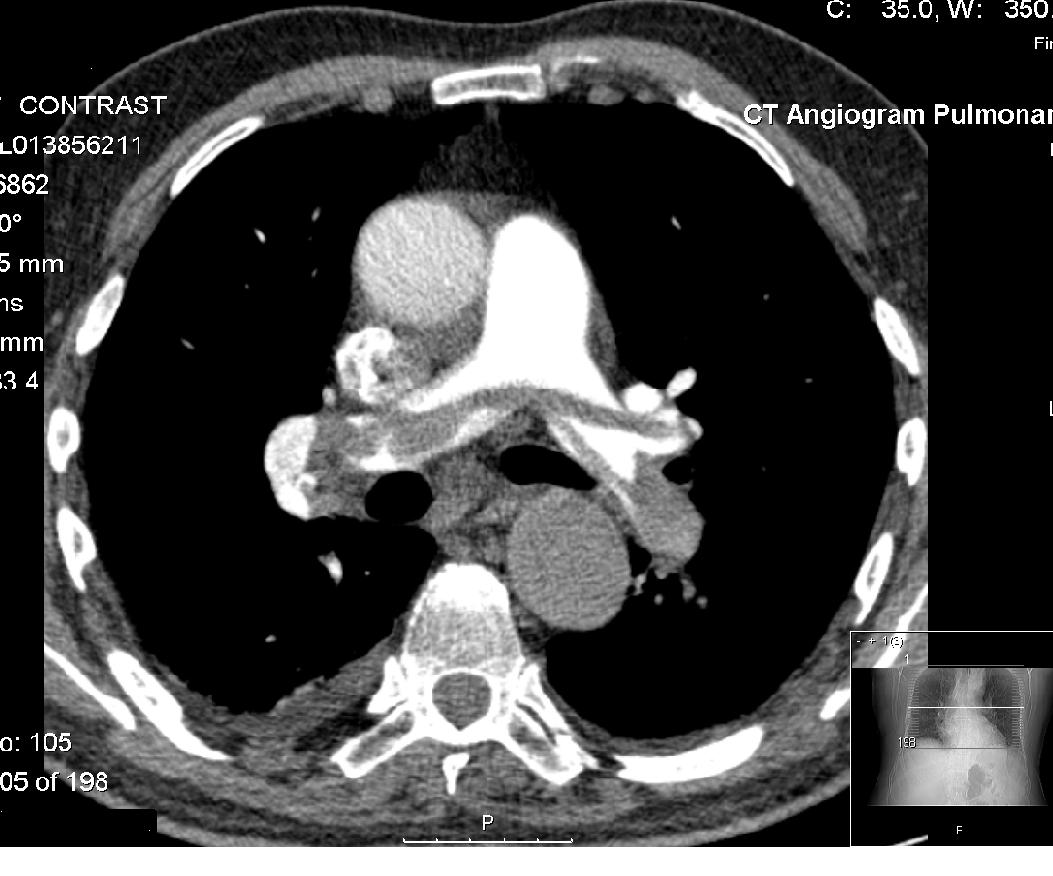
Cardiac images
However, a number of online anatomical models are becoming available. A single patient
 Models of cloth generally fall into three groups:
*The geometric-mechanical structure at
Models of cloth generally fall into three groups:
*The geometric-mechanical structure at

 A virtual world is an
A virtual world is an
/ref> Thus it is important that jurors and other legal decision-makers be made aware that such exhibits are merely a representation of one potential sequence of events.
Recent Advances in Augmented Reality
''Computers & Graphics'', November 2001. Sometimes CGI on TV with correct alignment to the real world has been referred to as
A Critical History of Computer Graphics and Animation
– a course page at
CG101: A Computer Graphics Industry Reference
Unique and personal histories of early computer graphics production, plus a comprehensive foundation of the industry for all reading levels. *
', by Anne Thompson, Wired, February 2005.
"History Gets A Computer Graphics Make-Over"
Tayfun King, ''Click'', BBC World News (2004-11-19)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Computer-Generated Imagery Visual effects Special effects
art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
, printed media, simulators
A simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. Simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the ...
, videos and video games. These images are either static (i.e. still image
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
s) or dynamic (i.e. moving images). CGI both refers to 2D computer graphics and (more frequently) 3D computer graphics with the purpose of designing characters, virtual world
A virtual world (also called a virtual space) is a computer-simulated environment which may be populated by many users who can create a personal avatar, and simultaneously and independently explore the virtual world, participate in its activities ...
s, or scenes and special effects (in film
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere ...
s, television programs, commercials, etc.). The application of CGI for creating/improving animation
Animation is a method by which image, still figures are manipulated to appear as Motion picture, moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent cel, celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited ...
s is called ''computer animation'', or ''CGI animation''.
History
The first feature film to use CGI as well as the composition of live-action film with CGI was '' Vertigo'', which used abstract computer graphics by John Whitney in the opening credits of the film. The first feature film to make use of CGI with live action in the storyline of the film was the 1973 film '' Westworld''. Other early films that incorporated CGI include '' Star Wars: Episode IV'' (1977), '' Tron'' (1982), '' Star Trek II: The Wrath of Khan '' (1982), '' Golgo 13: The Professional'' (1983), '' The Last Starfighter'' (1984), ''Young Sherlock Holmes
''Young Sherlock Holmes'' (also known with the title card name of "''Young Sherlock Holmes and the Pyramid of Fear''") is a 1985 American mystery adventure film directed by Barry Levinson and written by Chris Columbus, based on the characters ...
'' (1985), '' The Abyss'' (1989), '' Terminator 2: Judgement Day'' (1991), ''Jurassic Park
''Jurassic Park'', later also referred to as ''Jurassic World'', is an American science fiction media franchise created by Michael Crichton and centered on a disastrous attempt to create a theme park of cloned dinosaurs. It began in 1990 when ...
'' (1993) and '' Toy Story'' (1995). The first music video
A music video is a video of variable duration, that integrates a music song or a music album with imagery that is produced for promotion (marketing), promotional or musical artistic purposes. Modern music videos are primarily made and used as a m ...
to use CGI was Will Powers
Will Powers was the stage name used by celebrity photographer Lynn Goldsmith when she created a self-help comedy music album. The 1983 album, entitled ''Dancing for Mental Health'', used affirmations set to music to poke fun at the self-hel ...
' '' Adventures in Success'' (1983).
 Prior to CGI being prevalent in film, virtual reality, personal computing and gaming, one of the early practical applications of CGI was for aviation and military training namely, the flight simulator. Visual systems developed in flight simulators were also an important precursor to three dimensional computer graphics and Computer Generated Imagery (CGI) systems today. Namely because the object of flight simulation was to reproduce on the ground the behavior of an aircraft in flight. Much of this reproduction had to do with believable visual synthesis that mimicked reality. The Link Digital Image Generator (DIG) by the Singer Company (Singer-Link), was considered one of the worlds first generation CGI systems. It was a real-time, 3D capable, day/dusk/night system that was used by NASA shuttles, for F-111s, Black Hawk and the B-52. Link's Digital Image Generator had architecture to provide a visual system that realistically corresponded with the view of the pilot. The basic archictecture of the DIG and subsequent improvements contained a scene manager followed by geometric processor, video processor and into the display with the end goal of a visual system that processed realistic texture, shading, translucency capabilties, and free of aliasing.
Combined with the need to pair virtual synthesis with military level training requirements, CGI technologies applied in flight simulation were often years ahead of what would have been available in commercial computing or even in high budget film. Early CGI systems could depict only objects consisting of planar polygons. Advances in algorithms and electronics in flight simulator visual systems and CGI in the 1970s and 1980s influenced many technologies still used in modern CGI adding the ability to superimpose texture over the surfaces as well as transition imagery from one level of detail to the next one in a smooth manner.
The evolution of CGI led to the emergence of virtual cinematography in the 1990s, where the vision of the
Prior to CGI being prevalent in film, virtual reality, personal computing and gaming, one of the early practical applications of CGI was for aviation and military training namely, the flight simulator. Visual systems developed in flight simulators were also an important precursor to three dimensional computer graphics and Computer Generated Imagery (CGI) systems today. Namely because the object of flight simulation was to reproduce on the ground the behavior of an aircraft in flight. Much of this reproduction had to do with believable visual synthesis that mimicked reality. The Link Digital Image Generator (DIG) by the Singer Company (Singer-Link), was considered one of the worlds first generation CGI systems. It was a real-time, 3D capable, day/dusk/night system that was used by NASA shuttles, for F-111s, Black Hawk and the B-52. Link's Digital Image Generator had architecture to provide a visual system that realistically corresponded with the view of the pilot. The basic archictecture of the DIG and subsequent improvements contained a scene manager followed by geometric processor, video processor and into the display with the end goal of a visual system that processed realistic texture, shading, translucency capabilties, and free of aliasing.
Combined with the need to pair virtual synthesis with military level training requirements, CGI technologies applied in flight simulation were often years ahead of what would have been available in commercial computing or even in high budget film. Early CGI systems could depict only objects consisting of planar polygons. Advances in algorithms and electronics in flight simulator visual systems and CGI in the 1970s and 1980s influenced many technologies still used in modern CGI adding the ability to superimpose texture over the surfaces as well as transition imagery from one level of detail to the next one in a smooth manner.
The evolution of CGI led to the emergence of virtual cinematography in the 1990s, where the vision of the simulated
A simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. Simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the s ...
camera
A camera is an Optics, optical instrument that can capture an image. Most cameras can capture 2D images, with some more advanced models being able to capture 3D images. At a basic level, most cameras consist of sealed boxes (the camera body), ...
is not constrained by the laws of physics. Availability of CGI software and increased computer speeds have allowed individual artists and small companies to produce professional-grade films, games, and fine art from their home computers.
Static images and landscapes
 Not only do animated images form part of computer-generated imagery; natural looking landscapes (such as
Not only do animated images form part of computer-generated imagery; natural looking landscapes (such as fractal landscapes
A fractal landscape is a surface that is generated using a stochastic algorithm designed to produce fractal behavior that mimics the appearance of natural terrain. In other words, the result of the procedure is not a deterministic fractal surface, ...
) are also generated via computer algorithms
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing c ...
. A simple way to generate fractal surfaces is to use an extension of the triangular mesh method, relying on the construction of some special case of a de Rham curve, e.g., midpoint displacement
In mathematics, the blancmange curve is a self-affinity, self-affine curve constructible by midpoint subdivision. It is also known as the Takagi curve, after Teiji Takagi who described it in 1901, or as the Takagi–Landsberg curve, a generalizati ...
. For instance, the algorithm may start with a large triangle, then recursively zoom in by dividing it into four smaller Sierpinski triangles, then interpolate the height of each point from its nearest neighbors. The creation of a Brownian surface may be achieved not only by adding noise as new nodes are created but by adding additional noise at multiple levels of the mesh. Thus a topographical
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sci ...
map with varying levels of height can be created using relatively straightforward fractal algorithms. Some typical, easy-to-program fractals used in CGI are the ''plasma fractal'' and the more dramatic ''fault fractal''.
Many specific techniques have been researched and developed to produce highly focused computer-generated effects — e.g., the use of specific models to represent the chemical weathering of stones to model erosion and produce an "aged appearance" for a given stone-based surface.
Architectural scenes
 Modern architects use services from computer graphic firms to create 3-dimensional models for both customers and builders. These computer generated models can be more accurate than traditional drawings.
Modern architects use services from computer graphic firms to create 3-dimensional models for both customers and builders. These computer generated models can be more accurate than traditional drawings. Architectural animation
Architectural animation is a short architectural movie created on a computer. A computer-generated building is created along with landscaping and sometimes moving people and vehicles. Unlike an architectural rendering, which is a single image from ...
(which provides animated movies of buildings, rather than interactive images) can also be used to see the possible relationship a building will have in relation to the environment and its surrounding buildings. The processing of architectural spaces without the use of paper and pencil tools is now a widely accepted practice with a number of computer-assisted architectural design systems.
Architectural modeling tools allow an architect to visualize a space and perform "walk-throughs" in an interactive manner, thus providing "interactive environments" both at the urban and building levels. Specific applications in architecture not only include the specification of building structures (such as walls and windows) and walk-throughs but the effects of light and how sunlight will affect a specific design at different times of the day.
Architectural modeling tools have now become increasingly internet-based. However, the quality of internet-based systems still lags behind sophisticated in-house modeling systems.
In some applications, computer-generated images are used to "reverse engineer" historical buildings. For instance, a computer-generated reconstruction of the monastery at Georgenthal
Georgenthal is a municipality in the district of Gotha, in Thuringia, Germany. The former municipalities Leinatal, Hohenkirchen and Petriroda
Petriroda is a village and a former municipality in the district of Gotha, in Thuringia, Germany. Sin ...
in Germany was derived from the ruins of the monastery, yet provides the viewer with a "look and feel" of what the building would have looked like in its day.
Anatomical models
Scientific Computing and Imaging Institute
The Scientific Computing and Imaging (SCI) Institute is a permanent research institute at the University of Utah that focuses on the development of new scientific computing and visualization techniques, tools, and systems with primary application ...
have developed anatomically correct computer-based models. Computer generated anatomical models can be used both for instructional and operational purposes. To date, a large body of artist produced medical image
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
s continue to be used by medical students, such as images by Frank H. Netter, e.gCardiac images
However, a number of online anatomical models are becoming available. A single patient
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
is not a computer generated image, even if digitized. However, in applications which involve CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
s a three-dimensional model is automatically produced from many single-slice x-rays, producing "computer generated image". Applications involving magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
also bring together a number of "snapshots" (in this case via magnetic pulses) to produce a composite, internal image.
In modern medical applications, patient-specific models are constructed in 'computer assisted surgery'. For instance, in total knee replacement
Knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace the weight-bearing surfaces of the knee joint to relieve pain and disability, most commonly offered when joint pain is not diminished by conservative sources a ...
, the construction of a detailed patient-specific model can be used to carefully plan the surgery. These three-dimensional models are usually extracted from multiple CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
s of the appropriate parts of the patient's own anatomy. Such models can also be used for planning aortic valve implantations, one of the common procedures for treating heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, hea ...
. Given that the shape, diameter, and position of the coronary openings can vary greatly from patient to patient, the extraction (from CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
s) of a model that closely resembles a patient's valve anatomy can be highly beneficial in planning the procedure.
Cloth and skin images
 Models of cloth generally fall into three groups:
*The geometric-mechanical structure at
Models of cloth generally fall into three groups:
*The geometric-mechanical structure at yarn
Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, used in sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, ropemaking, and the production of textiles. Thread is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern manufact ...
crossing
*The mechanics of continuous elastic sheets
*The geometric macroscopic features of cloth.
To date, making the clothing of a digital character automatically fold in a natural way remains a challenge for many animators.
In addition to their use in film, advertising and other modes of public display, computer generated images of clothing are now routinely used by top fashion design firms.
The challenge in rendering human skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to most ...
images involves three levels of realism:
*Photo realism in resembling real skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
at the static level
*Physical realism in resembling its movements
*Function realism in resembling its response to actions.
The finest visible features such as fine wrinkle
A wrinkle, also known as a rhytid, is a fold, ridge or crease in an otherwise smooth surface, such as on skin or fabric. Skin wrinkles typically appear as a result of ageing processes such as glycation, habitual sleeping positions, loss of bo ...
s and skin pores are the size of about 100 μm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Unit ...
or 0.1 millimetre
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the electromagnetic spectrum, measured by the metre and its derived scales. The microwave is between 1 meter to 1 millimeter.
The millimetre (American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, ...
s. Skin can be modeled as a 7-dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a Space (mathematics), mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any Point (geometry), point within it. Thus, a Line (geometry), lin ...
al bidirectional texture function Bidirectional texture function (BTF) is a 6-dimensional function depending on planar texture coordinates (x,y) as well as on view and illumination spherical angles. In practice this function is obtained as a set of several thousand color images of ...
(BTF) or a collection of bidirectional scattering distribution function The definition of the BSDF (bidirectional scattering distribution function) is not well standardized. The term was probably introduced in 1980 by Bartell, Dereniak, and Wolfe.
Most often it is used to name the general mathematical function which de ...
(BSDF) over the target's surfaces.
Interactive simulation and visualization
Interactive visualization is the rendering of data that may vary dynamically and allowing a user to view the data from multiple perspectives. The applications areas may vary significantly, ranging from the visualization of the flow patterns influid dynamics
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids— liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including ''aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) an ...
to specific computer aided design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve co ...
applications. The data rendered may correspond to specific visual scenes that change as the user interacts with the system — e.g. simulators, such as flight simulator
A flight simulator is a device that artificially re-creates aircraft flight and the environment in which it flies, for pilot training, design, or other purposes. It includes replicating the equations that govern how aircraft fly, how they rea ...
s, make extensive use of CGI techniques for representing the world.''GPU-based interactive visualization techniques'' by Daniel Weiskopf 2006 pages 1-8
At the abstract level, an interactive visualization process involves a "data pipeline" in which the raw data is managed and filtered to a form that makes it suitable for rendering. This is often called the "visualization data". The visualization data is then mapped to a "visualization representation" that can be fed to a rendering system. This is usually called a "renderable representation". This representation is then rendered as a displayable image. As the user interacts with the system (e.g. by using joystick controls to change their position within the virtual world) the raw data is fed through the pipeline to create a new rendered image, often making real-time computational efficiency a key consideration in such applications.
Computer animation
While computer-generated images of landscapes may be static, ''computer animation
Computer animation is the process used for digitally generating animations. The more general term computer-generated imagery (CGI) encompasses both static scenes (still images) and dynamic images (moving images), while computer animation refe ...
'' only applies to dynamic images that resemble a movie. However, in general, the term computer animation refers to dynamic images that do not allow user interaction, and the term virtual world
A virtual world (also called a virtual space) is a computer-simulated environment which may be populated by many users who can create a personal avatar, and simultaneously and independently explore the virtual world, participate in its activities ...
is used for the interactive animated environments.
Computer animation is essentially a digital successor to the art of stop motion animation of 3D models and frame-by-frame animation of 2D illustrations. Computer generated animations are more controllable than other more physically based processes, such as constructing miniatures for effects shots or hiring extras for crowd scenes, and because it allows the creation of images that would not be feasible using any other technology. It can also allow a single graphic artist to produce such content without the use of actors, expensive set pieces, or props.
To create the illusion of movement, an image is displayed on the computer screen and repeatedly replaced by a new image which is similar to the previous image, but advanced slightly in the time domain (usually at a rate of 24 or 30 frames/second). This technique is identical to how the illusion of movement is achieved with television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertisin ...
and motion pictures.
Text-to-image models
Virtual worlds

 A virtual world is an
A virtual world is an agent-based
An agent-based model (ABM) is a computational model for simulating the actions and interactions of autonomous agents (both individual or collective entities such as organizations or groups) in order to understand the behavior of a system and wha ...
and simulated environment
Virtual reality (VR) is a simulated experience that employs pose tracking and 3D near-eye displays to give the user an immersive feel of a virtual world. Applications of virtual reality include entertainment (particularly video games), educa ...
allowing users to interact with artificially animated characters (e.g software agent) or with other physical users, through the use of avatars
Avatar (, ; ), is a concept within Hinduism that in Sanskrit literally means "descent". It signifies the material appearance or incarnation of a powerful deity, goddess or spirit on Earth. The relative verb to "alight, to make one's appearance ...
. Virtual worlds are intended for its users
Ancient Egyptian roles
* User (ancient Egyptian official), an ancient Egyptian nomarch (governor) of the Eighth Dynasty
* Useramen, an ancient Egyptian vizier also called "User"
Other uses
* User (computing), a person (or software) using an ...
to inhabit and interact, and the term today has become largely synonymous with interactive 3D virtual environments, where the users take the form of avatar
Avatar (, ; ), is a concept within Hinduism that in Sanskrit literally means "descent". It signifies the material appearance or incarnation of a powerful deity, goddess or spirit on Earth. The relative verb to "alight, to make one's appearanc ...
s visible to others graphically. These avatars are usually depicted as textual, two-dimensional, or three-dimensional graphical representations, although other forms are possible (auditory and touch sensations for example). Some, but not all, virtual worlds allow for multiple users.
In courtrooms
Computer-generated imagery has been used in courtrooms, primarily since the early 2000s. However, some experts have argued that it is prejudicial. They are used to help judges or the jury to better visualize the sequence of events, evidence or hypothesis. However, a 1997 study showed that people are poor intuitive physicists and easily influenced by computer generated images./ref> Thus it is important that jurors and other legal decision-makers be made aware that such exhibits are merely a representation of one potential sequence of events.
Broadcast and live events
Weather visualizations were the first application of CGI in television. One of the first companies to offer computer systems for generating weather graphics wasColorGraphics Weather Systems ColorGraphics Weather Systems was a computer graphics company that pioneered the use of computer graphics for displaying weather forecasts on local television. Formed in 1979 by Terry Kelly and Richard Daly, it is now part of Weather Central, anothe ...
in 1979 with the "LiveLine", based around an Apple II
The Apple II (stylized as ) is an 8-bit home computer and one of the world's first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products. It was designed primarily by Steve Wozniak; Jerry Manock developed the design of Apple II's foam-m ...
computer, with later models from ColorGraphics using Cromemco
Cromemco was a Mountain View, California microcomputer company known for its high-end Zilog Z80, Z80-based S-100 bus computers and peripherals in the early days of the personal computer revolution.
The company began as a partnership in 1974 betwe ...
computers fitted with their Dazzler video graphics card.
It has now become common in weather casting to display full motion video of images captured in real-time from multiple cameras and other imaging devices. Coupled with 3D graphics symbols and mapped to a common virtual geospatial model, these animated visualizations constitute the first true application of CGI to TV.
CGI has become common in sports telecasting. Sports and entertainment venues are provided with see-through and overlay content through tracked camera feeds for enhanced viewing by the audience. Examples include the yellow " first down" line seen in television broadcasts of American football
American football (referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada), also known as gridiron, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end. The offense, the team with ...
games showing the line the offensive team must cross to receive a first down. CGI is also used in association with football and other sporting events to show commercial advertisements overlaid onto the view of the playing area. Sections of rugby
Rugby may refer to:
Sport
* Rugby football in many forms:
** Rugby league: 13 players per side
*** Masters Rugby League
*** Mod league
*** Rugby league nines
*** Rugby league sevens
*** Touch (sport)
*** Wheelchair rugby league
** Rugby union: 1 ...
fields and cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
pitches also display sponsored images. Swimming telecasts often add a line across the lanes to indicate the position of the current record holder as a race proceeds to allow viewers to compare the current race to the best performance. Other examples include hockey puck tracking and annotations of racing car performance and snooker ball trajectories. Azuma, Ronald; Balliot, Yohan; Behringer, Reinhold; Feiner, Steven; Julier, Simon; MacIntyre, BlairRecent Advances in Augmented Reality
''Computers & Graphics'', November 2001. Sometimes CGI on TV with correct alignment to the real world has been referred to as
augmented reality
Augmented reality (AR) is an interactive experience that combines the real world and computer-generated content. The content can span multiple sensory modalities, including visual, auditory, haptic, somatosensory and olfactory. AR can be de ...
.
Motion capture
Computer-generated imagery is often used in conjunction withmotion capture
Motion capture (sometimes referred as mo-cap or mocap, for short) is the process of recording the movement of objects or people. It is used in military, entertainment, sports, medical applications, and for validation of computer vision and robo ...
to better cover the faults that come with CGI and animation. Computer-generated imagery is limited in its practical application by how realistic it can look. Unrealistic, or badly managed computer-generated imagery can result in the uncanny valley effect. This effect refers to the human ability to recognize things that look eerily like humans, but are slightly off. Such ability is a fault with normal computer-generated imagery which, due to the complex anatomy of the human body, can often fail to replicate it perfectly. Artists can use motion capture to get footage of a human performing an action and then replicate it perfectly with computer-generated imagery so that it looks normal.
The lack of anatomically correct digital models contributes to the necessity of motion capture as it is used with computer-generated imagery. Because computer-generated imagery reflects only the outside, or skin, of the object being rendered, it fails to capture the infinitesimally small interactions between interlocking muscle groups used in fine motor skills like speaking. The constant motion of the face as it makes sounds with shaped lips and tongue movement, along with the facial expressions that go along with speaking are difficult to replicate by hand. Motion capture can catch the underlying movement of facial muscles and better replicate the visual that goes along with the audio.
See also
References
Citations
Sources
* * * *External links
A Critical History of Computer Graphics and Animation
– a course page at
Ohio State University
The Ohio State University, commonly called Ohio State or OSU, is a public land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio. A member of the University System of Ohio, it has been ranked by major institutional rankings among the best publ ...
that includes all the course materials and extensive supplementary materials (videos, articles, links).
CG101: A Computer Graphics Industry Reference
Unique and personal histories of early computer graphics production, plus a comprehensive foundation of the industry for all reading levels. *
', by Anne Thompson, Wired, February 2005.
"History Gets A Computer Graphics Make-Over"
Tayfun King, ''Click'', BBC World News (2004-11-19)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Computer-Generated Imagery Visual effects Special effects
imagery
Imagery is visual symbolism, or figurative language that evokes a mental image or other kinds of sense impressions, especially in a literary work, but also in other activities such as psychotherapy.
Forms
There are five major types of sensory ima ...
Articles containing video clips